The Moment I Learned Regular Plywood Has Limits
Years ago, I trimmed out a wall beside a freestanding wood stove using “good” birch cabinet-grade plywood. Looked flawless for a month—then the edge nearest the stove started to darken. Eventually, the veneer bubbled like toast under a broiler. Nothing caught fire, but the message was clear: standard plywood and steady heat don’t mix.
Ever since, I’ve kept a short list of materials that can take the heat—literally. If your next project sits near a range, fireplace, furnace, or grill, this guide will help you choose heat-resistant plywood that won’t warp, scorch, or fail inspection.
What Is Heat-Resistant Plywood?
In plain English, heat-resistant plywood is plywood engineered to survive high temperatures without structural or cosmetic failure. Most builders and code officials call it fire-retardant-treated plywood (FRT) or phenolic film-faced plywood.
Fire-retardant plywood is pressure-impregnated with chemicals that slow ignition and reduce flame spread. Instead of flashing into flame, it chars gradually, buying valuable minutes in a fire event. These panels are often tested under ASTM E84 standards and rated Class A or Class B, depending on performance.
Phenolic-faced plywood uses resin-saturated films that create a tough, heat-resistant exterior, perfect for workshops, trailers, or outdoor cabinetry.
For background on how plywood layers are built and bonded, see Plywood Grades Explained.
🔗The U.S. Forest Products Laboratory defines fire-retardant wood as material treated to “reduce the flammability of wood and delay its combustion.” Source: Forest Plywood
Where It Makes Sense (and Where It Doesn’t)
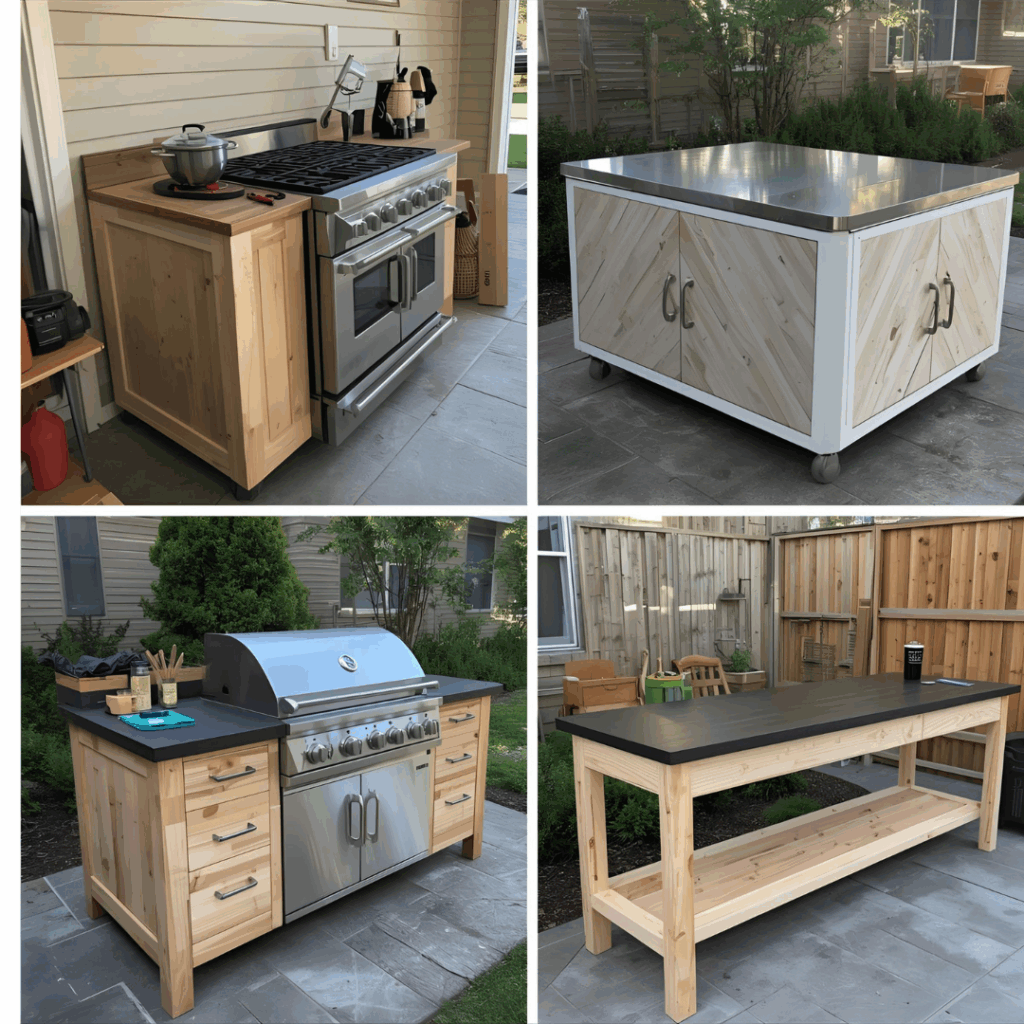

Best Uses
- Kitchen side panels, range surrounds, or wall ends near cooktops – Great for giving the kitchen a built-in, professional look without worrying about heat discoloration or delamination.
- Fireplaces and pellet-stove walls (with required clearance) – It stands up well behind decorative trim, where radiant heat can easily ruin cheaper materials.
- Outdoor kitchens and smoker enclosures – The right panel will shrug off both humidity and the warmth that radiates during long weekend cooks.
- RV, camper, and van interiors that bake in sunlight – Perfect for lightweight builds that face daily temperature swings without warping.
- Workshop benches for soldering or epoxy curing – They resist the brief but intense heat from tools, making cleanup and maintenance a breeze.
- Stairwells or corridors requiring a flame-spread rating – Many builders use it to quietly meet code without changing the look or finish of the space.
Avoid Using It
- As a direct stove backer without an air gap or barrier – Even the best-treated plywood can’t survive constant direct heat, and you’ll eventually see scorch marks or worse.
- In saunas or steam rooms (moisture + heat = separate design problem) – The trapped humidity will break down treatments over time and cause surface bubbling.
- When building assemblies that require non-combustible materials such as cement board or gypsum, Inspectors will fail that installation instantly, since heat-resistant doesn’t mean fireproof.
If you’re unsure whether plywood is allowed in a particular location, check NFPA 703 (Fire Retardant Treated Wood Standard) or your local building department’s fire-resistance tables.
FRT vs. Phenolic: Choosing the Right Type

When you’re standing at the lumber rack, both panels might just look like plywood sheets — but they behave very differently once the heat’s on. Here’s how I usually decide between the main types based on real-world use, not just labels.
| Type | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| FRT Plywood | This version is soaked under pressure with special fire-retardant salts that soak deep into the wood fibers. You can still cut, screw, and paint it like normal plywood, but it reacts slower to heat and open flame. | It slows flame spread dramatically, takes paint or primer well, and usually passes code where a Class A rating is required. | You do have to follow the manufacturer’s install guidelines exactly — and every cut edge must be sealed, or the treatment won’t protect that area. |
| Phenolic Film-Faced Plywood | Instead of chemical treatment, these sheets are wrapped in a thin, heat-resistant resin film — often a dark brown or black layer with a slick texture. It’s common in trailer floors, concrete forms, and heavy-use benches. | The surface laughs off moisture, glue spills, and radiant heat, which makes cleanup simple and lifespan long. | Painting it can be tricky since the resin film is nonporous, and it doesn’t carry an official “fire rating,” even though it performs well near heat. |
| Marine-Grade FRT Plywood | This is the top-shelf hybrid: marine-grade veneers bonded with waterproof adhesive and then treated for flame resistance. It’s made for boats, outdoor kitchens, or anywhere humidity and heat meet. | It handles coastal air, steam, and sudden temperature swings without swelling or delaminating — a lifesaver in damp climates. | This version is soaked under pressure with special fire-retardant salts that soak deep into the wood fibers. You can still cut, screw, and paint it like normal plywood, but it reacts more slowly to heat and open flame. |
Real-World Field Tips
Installation Tips:
- Keep your clearances. Heat-resistant plywood buys you time, not immunity. Always respect the appliance’s minimum distance to combustibles. I’ve seen projects fail inspection simply because someone tried to save an inch of space.
- Seal every cut edge. After trimming, brush on intumescent paint or high-temp silicone so moisture and oxygen can’t sneak in. That small detail keeps the treatment from breaking down over time.
- Use proper fasteners. Stainless or coated screws prevent chemical reactions with FRT salts. Cheap screws can stain or corrode faster than you think, especially in humid spots.
- Add an air gap. A ¾-inch gap backed with mineral wool insulation drastically lowers surface temperature. Even a slim cavity makes a huge difference when you test it with an infrared thermometer.
- Finish wisely. Ordinary latex will yellow near heat—opt for heat-resistant enamel or a clear high-temp polyurethane. Those coatings stay clean longer and won’t get tacky under warm conditions.
- Label and document. Keep manufacturer paperwork; some inspectors will ask for the exact FRT spec sheet. Having proof on hand saves a lot of explaining during walk-throughs.
- Ventilate hot zones. A simple vent slot at the top and bottom of a panel lets heat escape instead of cooking the wood. You’ll feel the difference in airflow the first time the appliance runs hot.
🔗 Century Ply – 5 Reasons to Opt for Fire-Retardant Plywood explains how modern FRT boards resist both moisture and flame spread.
My Shop Tests and Results
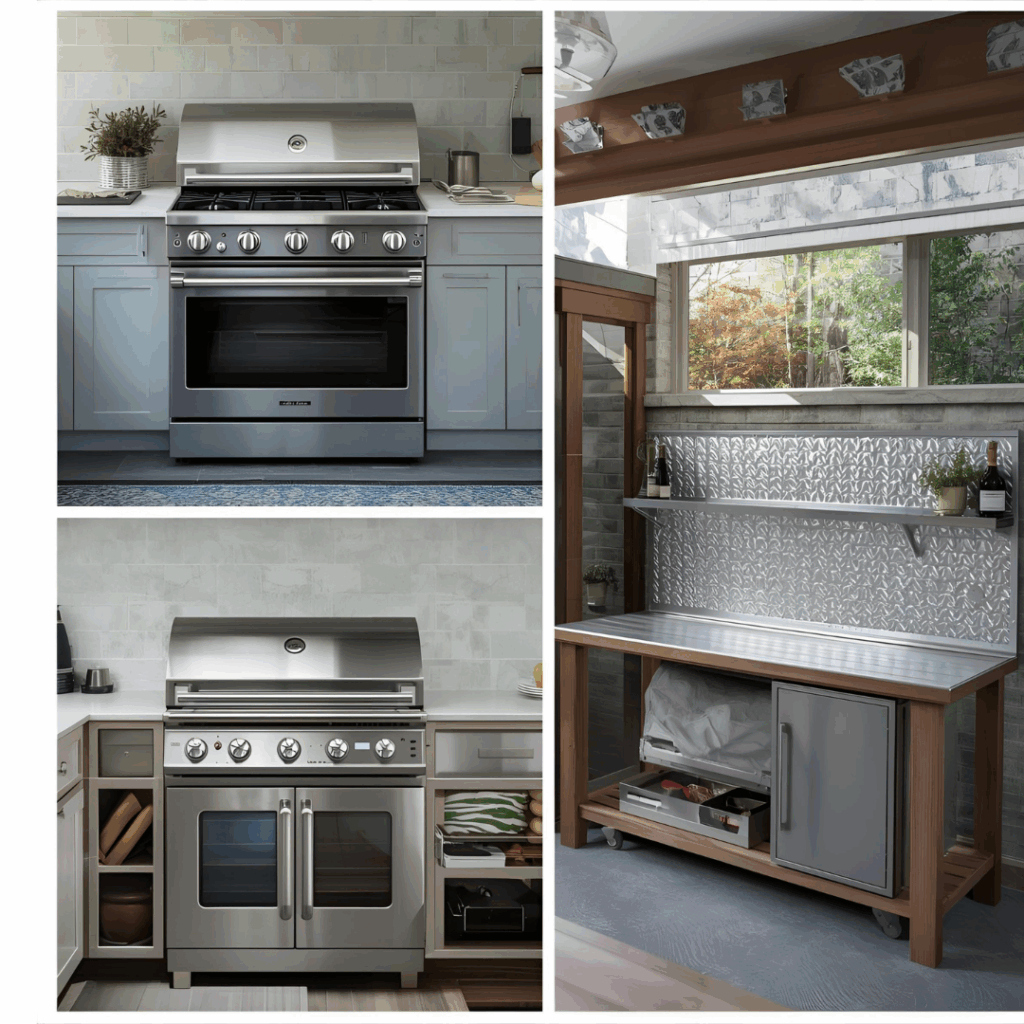

My Shop Tests and Results
- Behind a range: I used phenolic-faced plywood as a hidden backer behind stainless trim. After three years, no discoloration or delamination. It’s one of those fixes you forget about entirely because it just works, even through daily cooking heat.
- Outdoor smoker cabinet: ¾″ FRT carcass plus mineral wool layer and small vent slots. Even after all-night cooks, the exterior panel stays below 100 °F. The setup has survived Florida humidity and constant smoke without a single warp or soft spot.
- Workbench “hot zone”: 21 mm phenolic plywood top with a thin, removable aluminum sheet. I’ve hit it with a soldering iron—no bubbling, no smell. It’s still my favorite work surface because cleanup takes seconds, and it never shows burn marks.
For step-by-step moisture-proofing and sealing, similar to what you’ll do on hot builds, check ‘Preparing a Plywood Subfloor for Tile‘.
Installation Walk-Through
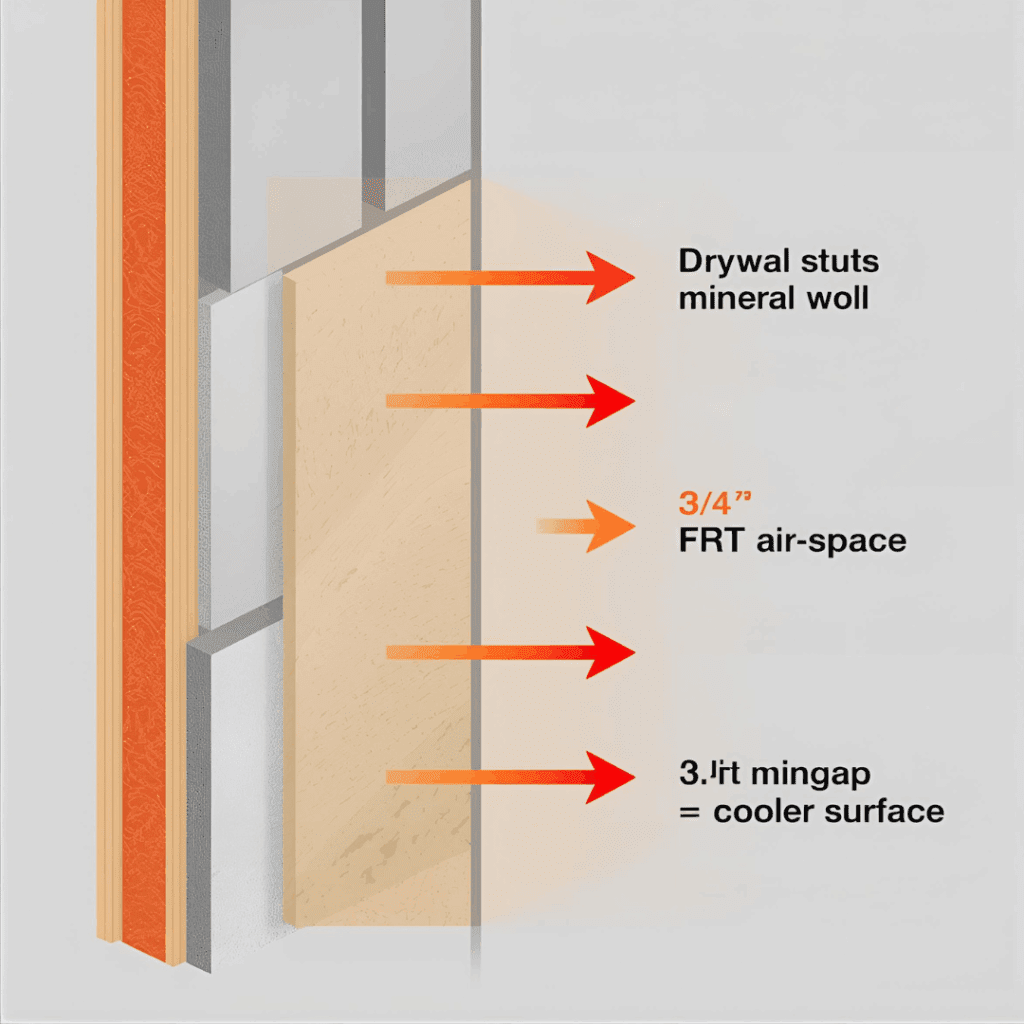
Installation Walk-Through

- Mark your studs and pre-drill mounting holes before sealing edges. It saves you from fighting the drill once the sealer has dried and hardened around the perimeter.
- Apply heat-rated adhesive or fasten mechanically; avoid cheap construction glue—it softens around 150 °F (see Liquid Nails vs. Wood Glue for adhesive performance data). A small upgrade in adhesive here keeps your panels tight for years, even through daily heat cycles.
- Create a ¾″ air space with wood strips or steel furring. That narrow gap works like a hidden shield, cutting surface temperature more than most people expect.
- Install mineral wool batts (ROCKWOOL Safe’n’Sound or equivalent). It’s one of the simplest ways to trap heat and sound while keeping everything behind the panel cool to the touch.
- Fasten panels loosely, allowing for minor thermal movement. Wood still expands when warm, and a bit of flexibility prevents cracking or squeaks down the road.
- Finish with high-temp coating—intumescent paint is a good insurance policy even where code doesn’t require it. It adds a subtle layer of protection and peace of mind, especially for DIY builds near open heat.
Product Picks (Affiliate-Friendly)
| Product | Description | Link |
|---|---|---|
| Hoover Fire-Retardant CDX 5/8″ 4×8 | Certified Class A FRT plywood for walls and ceilings | Amazon |
| FlameFreez Pressure-Treated Plywood 5/8″ 4×8 | Outdoor-capable FRT sheathing | Amazon |
| Phenolic Film-Faced Hexa Plywood (24×48) | Heat-resistant, anti-slip phenolic surface; perfect for benches | Amazon |
| ROCKWOOL Mineral Wool Batts | Non-combustible insulation for air-gap cavities | Amazon |
| High-Temp Intumescent Paint | Expands under heat to seal and protect edges | Amazon |
Disclosure: As an Amazon Associate, ThePlywood.com earns from qualifying purchases.
Comparing Regular vs Heat-Resistant Plywood
| Feature | Standard Plywood | Heat-Resistant Plywood |
|---|---|---|
| Adhesive | Urea-formaldehyde | Phenolic or melamine resin |
| Flame Spread Index | 200+ (untreated) | ≤ 25 (Class A) |
| Smoke Development | High | Low |
| Moisture Resistance | Variable | Often exterior-grade |
| Finish Compatibility | All paints | Prefer high-temp or intumescent |
| Cost | Lower | ~25–40% higher |
Maintenance Routine
- Annual inspection: Check for warping, cracking, or darkening.
- Clean gently: Use mild soap and water; avoid harsh solvents that may strip retardant coatings.
- Re-seal edges: Every couple of years, brush on more high-temp silicone or paint.
- Keep ventilation clear: Dust and grease buildup hold heat—especially in kitchens.
Environmental and Safety Notes
Modern treatments use phosphate or borate compounds, not formaldehyde or halogens, so FRT panels today are safe for indoor use. Look for FSC-certified or EPA-compliant products to keep your project eco-responsible.
🔗 Wigwam Ply – Fire-Resistant Plywood Benefits and Applications discusses newer, low-toxicity chemical formulations.
Quick FAQ
Is heat-resistant plywood fireproof?
No. It resists ignition and slows flame spread but remains combustible. Always follow clearance rules.
Can I paint or stain it?
Yes, but near heat, use high-temperature or intumescent coatings and reseal every cut edge.
Will it pass building inspection?
If labeled FRT and backed by manufacturer documentation, it typically satisfies code for flame-spread requirements—but always verify with your AHJ.
Is it safe for kitchens?
Absolutely. Many high-end cabinet shops use Class A FRT plywood for range ends and vent-hood surrounds to meet safety standards.
Final Thoughts

Heat-resistant plywood is a quiet workhorse. You won’t notice it doing its job—but you’ll be grateful it does. Pairing Class A FRT panels or phenolic-faced boards with air gaps, mineral wool, sealed edges, and smart finishes keeps your project straight, safe, and inspection-ready for years.
If you want to dig deeper into finishes and bonding, explore surface durability tricks in How to Make Plywood Look Nice.
Build once. Build safe. And never underestimate what a few degrees of heat can do to the wrong panel.




